State-of-the-art model-based Reinforcement Learning (RL) approaches either use gradient-free,
population-based methods for planning, learned policy networks, or a combination of policy networks and
planning. Hybrid approaches that combine Model Predictive Control (MPC) with a learned model and a policy
prior to efficiently leverage the benefits of both paradigms have shown promising results. However, these
hybrid approaches typically rely on gradient-free optimization methods, which can be computationally
expensive for high-dimensional control tasks.
While gradient-based methods are a promising approach, recent works have empirically shown that
gradient-based methods often perform worse than their gradient-free counterparts due to the fact that
gradient-based methods can converge to suboptimal local optima and are prone to exploding or vanishing
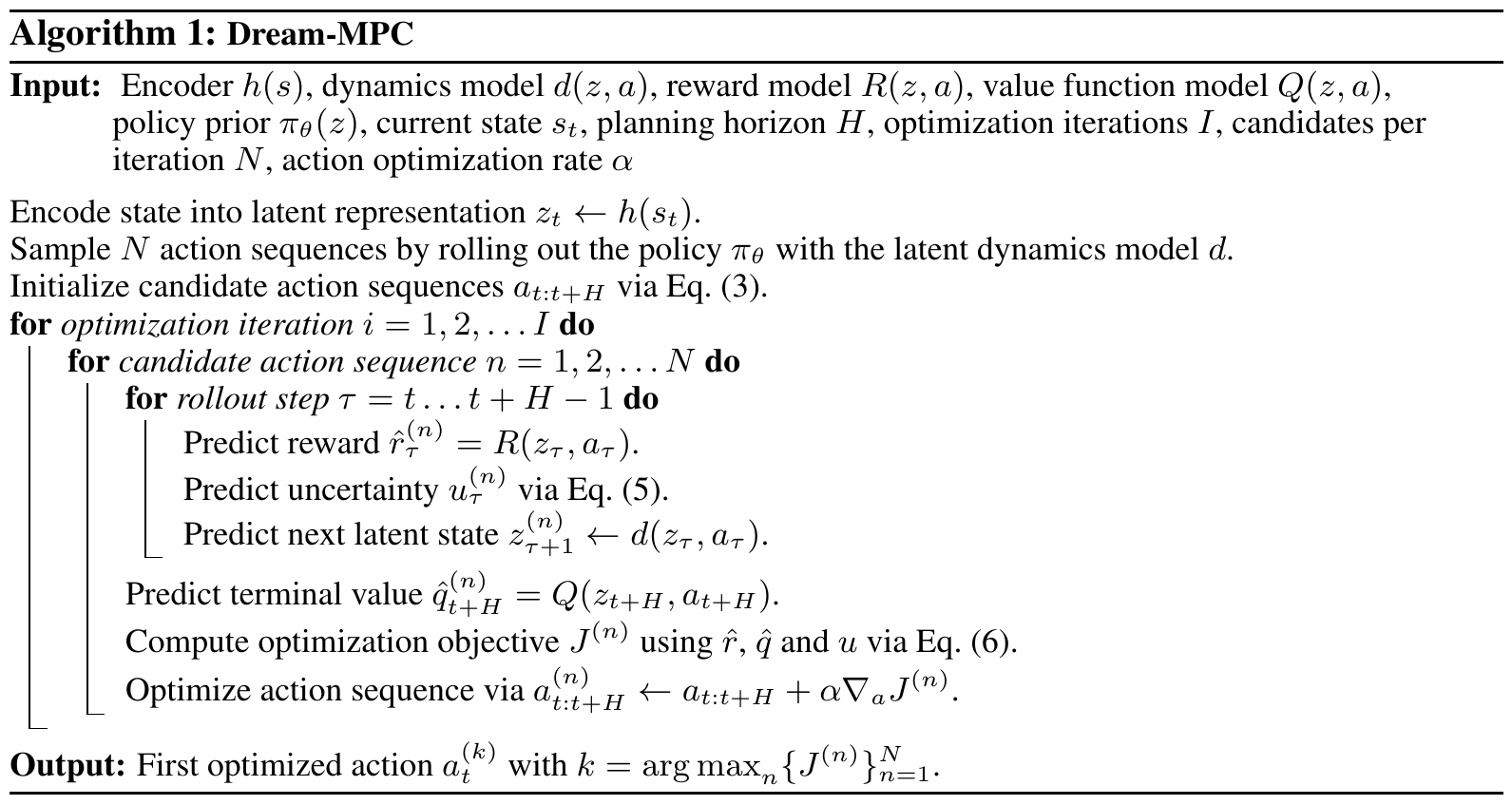
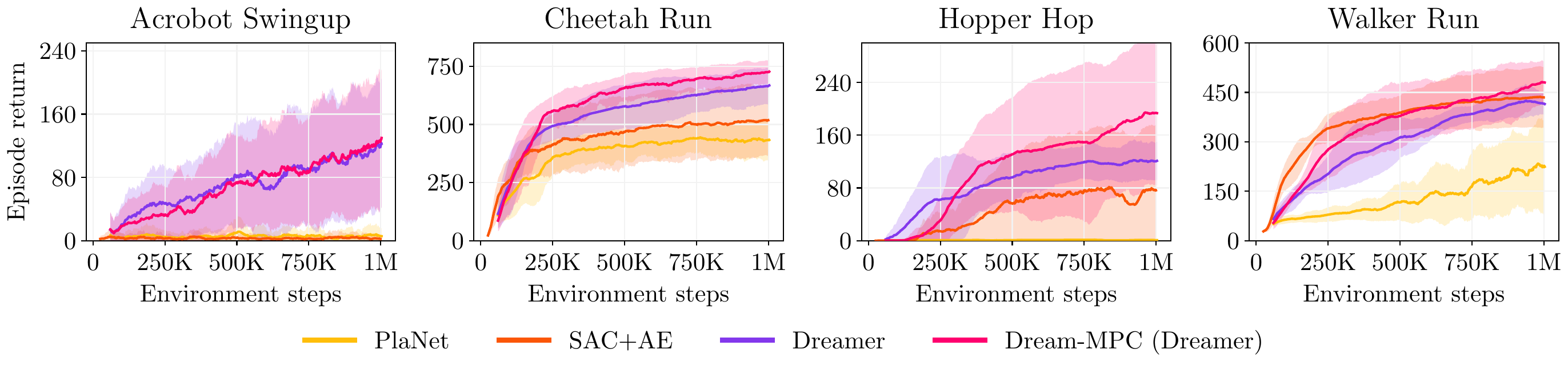
gradients. We propose Dream-MPC, a novel approach that generates few candidate trajectories from a
rolled-out policy and optimizes each trajectory by gradient ascent using a learned world model.
We incorporate uncertainty regularization directly into the optimization objective and amortize
optimization iterations over time by reusing previously optimized actions. We evaluate our method on
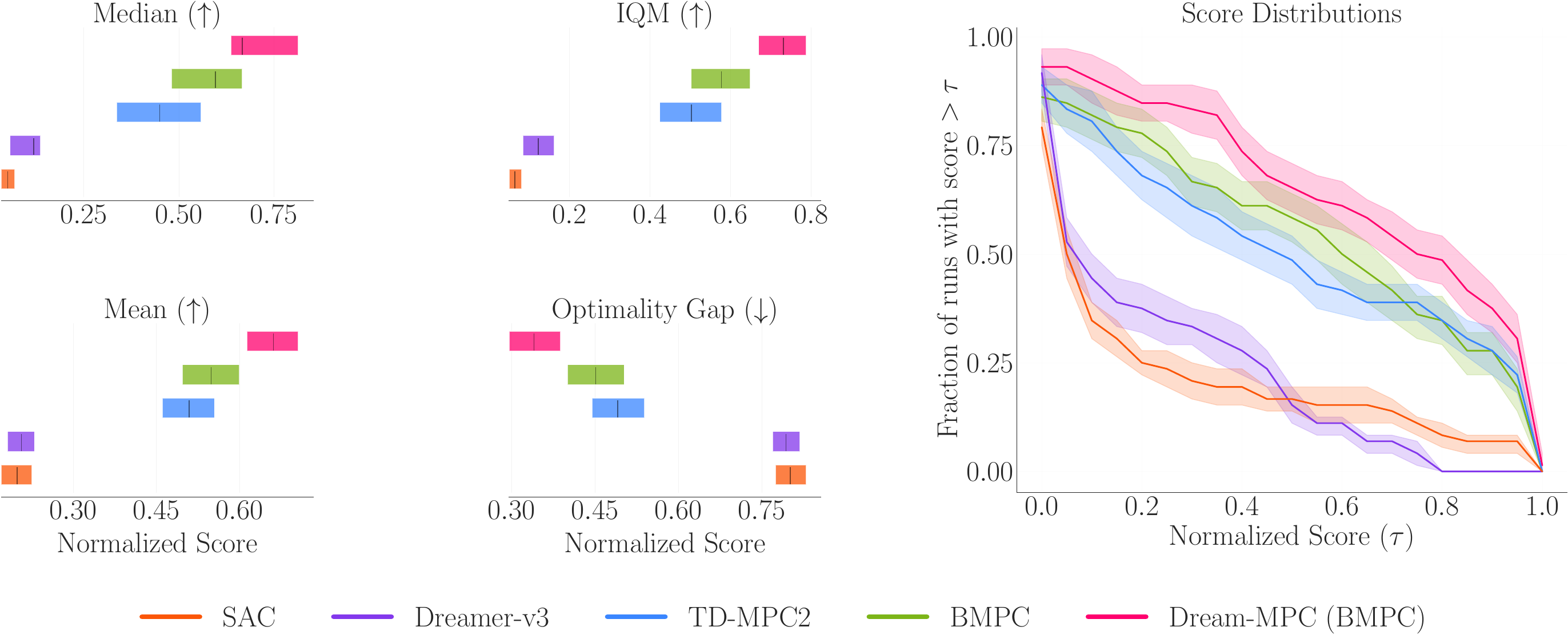
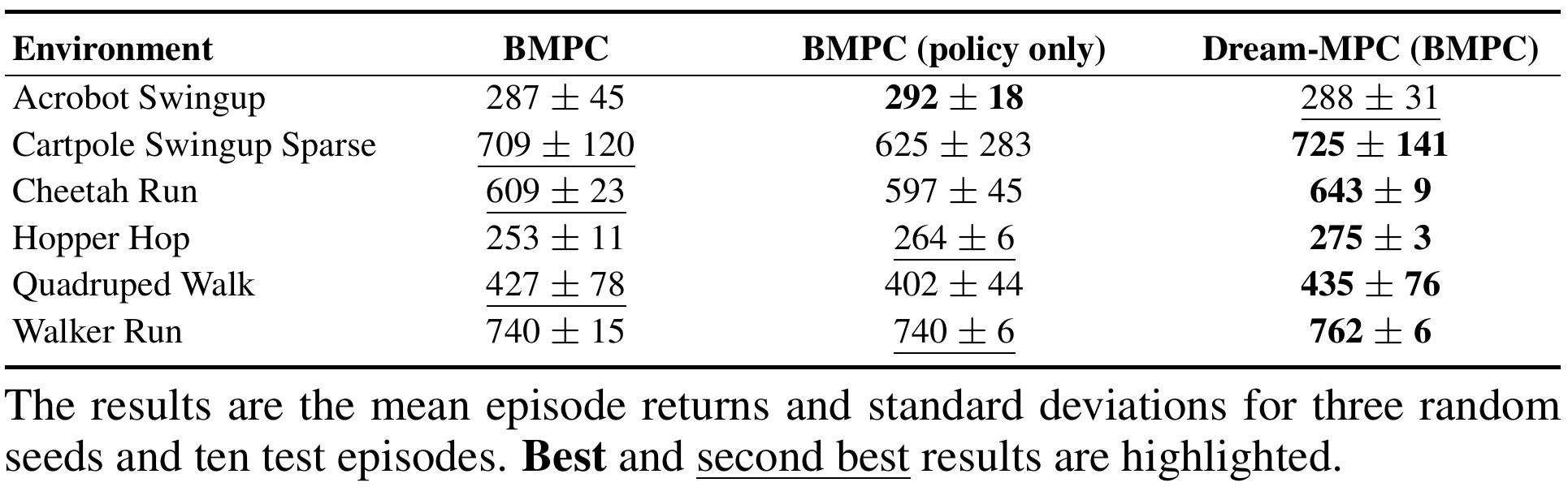
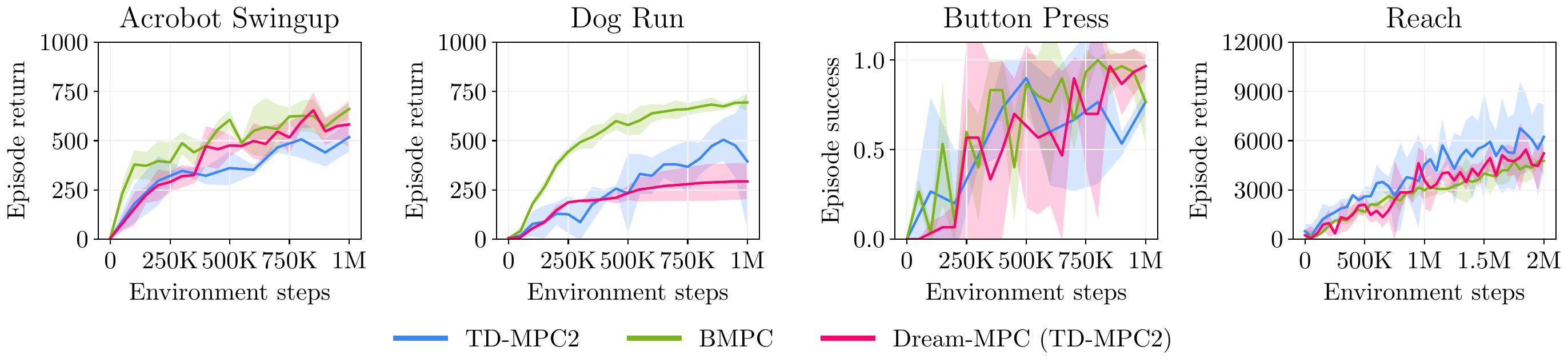
multiple continuous control tasks from the DeepMind Control Suite, Meta-World and HumanoidBench and show
that gradient-based MPC can significantly improve the performance of the underlying policy and can
outperform gradient-free MPC and state-of-the-art baselines.